Serrano Indians
The territory of the Serrano included the entire San Bernardino range of mountains, west into the San Gabriel mountains to North Baldy (Mt Baden-Powell), south across the San Bernardino Valley and eastward to near 29 Palms and the Oasis of Mara.Traditional Territory
The territorial claims of the different ethnic groups who occupied the Mojave and ...Oral History
A version of the Serrano creation story told by elder Dorothy Ramon describes ...
Claims Case Boundaries
the descriptions agreed to by the tribes themselves in ...
Subsistence Resources
Plant Resources
Bean and Saubel's Temelpakh (1972), which pertains to the ethnobotany of the Cahuilla contains much information applicable to the Serrano as well. ...
Animal Resources
Dorothy Ramon has provided information about how the Serrano traditionally went about procuring and using ...
Material Culture, Technology
The Serranos acquired the many species of large and small animals available in the area with ...Trade, Exchange, Storage
Their principal trading partners were the Mojave to the east and the Gabrielino to the west, but they also traded with ...Social structure
... each of whom belonged to either of two exogamous moieties, Coyote or Wildcat. Each clan was composed of ...Religion, World View
Serrano world view, like its culture in general, is less well known than that of some of their neighbors, such as the ...History
-
Mission Period
The Serrano were a fairly numerous people when the Spanish arrived in 1769, but beginning about 1790, the ...
-
American Period
It has been suggested that the Serrano left the area in the early 1860s when a smallpox epidemic struck ...
-
Present Day Serrano
Morongo Indian Reservation probably has more Serranos than any other reservation, but since many ...
Contents >> Next >> from:
2002 The Native American Ethnography and Ethnohistory of Joshua Tree National Park, An Overview.
by Lowell John Bean, Ph.D. and Sylvia Brakke Vane, M.A.
Also see:
Sub-groups of the Serrano; Vanyume, Kitanemuk
Four Directions Institute
Ethnie: SERRANOLanguage: Northern Takic
Family: Takic
Stock: Uto-Aztecan
Phylum: Aztec-Tanoan
Macro-Culture: Southern California
Speakers 1 1994 C.J. Coker 1 has since learned language, several others learning The Takic peoples arrived in southern California about 2,500 years ago. All were peaceful hunter/gatherer mountain and desert cultures. The Serrano delineation was a result of the Spanish missionization that separated them from the so called Gabrielino and Kitanemuk, with whom they comprised the Northern Takic language group. The Serrano herein include the Vanyume and Alliklik. They ranged throughout the San Bernardino Mountains, as far as the San Gabriel as far west as Mt. San Antonio. Ancestors of the present Serrano may well have ranged south of those mountains from Sierra Madre to the Morongo Valley. They occupied the region of the Mojave River in the high desert to the north. The Serrano had close cultural ties to the Cahuilla, an late, were allies and trading partners with the Chemehuevi and indeed adopted at least one band of that ethnie into their culture.
Aboriginal Locations Akavat, Amaha-vit, Atu'aviatam, Kayuwat, Kupacha, Malki, Mara, Maringa, Mawaitum, Muhiatnim, Mukunpat, Nahyu, Palukiktam, Pihatupayam, Tuchahu, Tumunamtu, Turka, Wa'acham, Wakuhi, Yahaviat
Present Locations
MORONGO RESERVATION, Banning
SAN MANUAL RESERVATION, Highland
Year / History
1771 / Mission San Gabriel Arcangel founded
1772 / Pedro Fages entered territory
1776 / Garces arrived in territory
1812 / Revolted against missions along with Cahuilla and Yuma
1819 / Asistencia established near Redlands
1821 / Large number indentured to Mexican feudal barons
1834 / Many removed bodily to missions
1840 / Smallpox epidemic
1860 / Smallpox epidemic
1875 / Reservation established
1975 / 100 Claimed descent, per Bean and Smith
Year / Population / Source
1700 / 1,500 / NAHDB calculation
1770 / 1,500 / Kroeber estimate
1800 / 1,500 / NAHDB calculation
1900 / 100 / NAHDB calculation
1910 / 118 / Census
1975 / 100 / Claimed descent, per Bean and Smith
2000 / 150 / NAHDB calculation
Other speakers of the same language:
Gabrielino, Kitanemuk
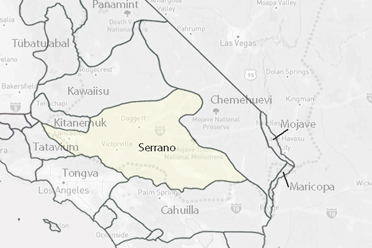
Native Location: Mojave Desert and the San Bernardino Mountains in Southern California
Food: Acorn, Manzanita berries, pine nuts, yucca, deer, rabbit
Language: Takic branch of Uto-Aztecan
Cultural Notes: They were once sedentary hunter-gatherers. Serrano is Spanish for "mountaineer", but they called themselves Yuharetum, which means "people of the pines."