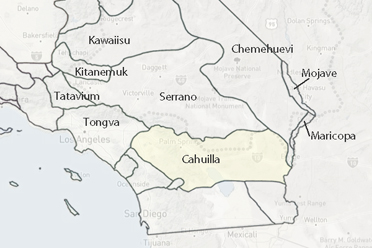
Cahuilla Indians
The Cahuilla people are indigenous to Southern California, with their traditional territory spanning from the Coachella Valley to the Salton Sea and extending into desert and mountain regions. They lived as hunter-gatherers, utilizing diverse plant and animal resources, and built seasonal homes depending on their needs. Their material culture included tools made from stone, wood, and bone, as well as baskets and pottery for storage and cooking. They maintained trade networks with neighboring tribes like the Halchidhoma and Gabrielino.Cahuilla society was structured into clans belonging to two moieties, Wildcat and Coyote, which influenced marriage and social organization. Their religious beliefs centered on power ("?iva?a") and a systematic but unpredictable universe. The creator gods Mukat and Temayawet played central roles in their cosmology, and various supernatural beings were tied to natural features.
Spanish and Mexican incursions in the late 18th century displaced some Cahuilla groups but did not significantly impact their way of life until the 19th century. By the 1870s, reservations were established, including Morongo, Agua Caliente, and Torres-Martinez, among others. Cahuillas resisted government efforts to suppress their cultural practices, such as traditional ceremonies. In the early 20th century, they became active in political movements like the Mission Indian Federation, which advocated for land rights and self-governance.
The Cahuilla adapted to changing economic conditions by engaging in agriculture, wage labor, and, later, casino enterprises. By the mid-20th century, many had left reservations due to poor living conditions, but government programs in the 1960s helped improve infrastructure. Today, the Cahuilla continue to maintain cultural traditions, including language preservation and museum initiatives like the Malki Museum at Morongo Reservation.
Serrano, Chemehuevi
Excerpts from;THE NATIVE AMERICANS OF JOSHUA TREE NATIONAL PARK AN ETHNOGRAPHIC OVERVIEW AND ASSESSMENT STUDY
by Cultural Systems Research, Inc. August 22, 2002;